https://www.jianshu.com/p/c2a361c2406c
六边形架构
六边形架构又称“端口和适配器模式”,是Alistair Cockburn提出的一种具有对称性特征的架构风格。在这种架构中,系统通过适配器的方式与外部交互,将应用服务于领域服务封装在系统内部。
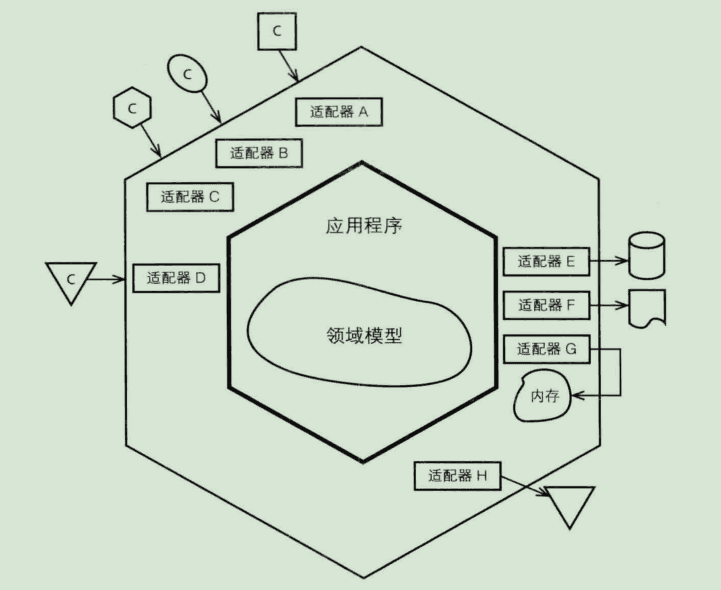
六边形架构还是一种分层架构,如上图所示,它被分为了三层:端口适配器、应用层与领域层。而端口又可以分为输入端口和输出端口。
- 输入端口
用于系统提供服务时暴露API接口,接受外部客户系统的输入,并客户系统的输入转化为程序内部所能理解的输入。系统作为服务提供者是对外的接入层可以看成是输入端口。
- 输出端口
为系统获取外部服务提供支持,如获取持久化状态、对结果进行持久化,或者发布领域状态的变更通知(如领域事件)。系统作为服务的消费者获取服务是对外的接口(数据库、缓存、消息队列、RPC调用)等都可以看成是输入端口。
- 应用层
定义系统可以完成的工作,很薄的一层。它并不处理业务逻辑通过协调领域对象或领域服务完成业务逻辑,并通过输入端口输出结果。也可以在这一层进行事物管理。
- 领域层
负责表示业务概念、规则与状态,属于业务的核心。
应用层与领域层的不变性可以保证核心领域不受外部的干扰,而端口的可替换性可以很方便的对接不用的外部系统。
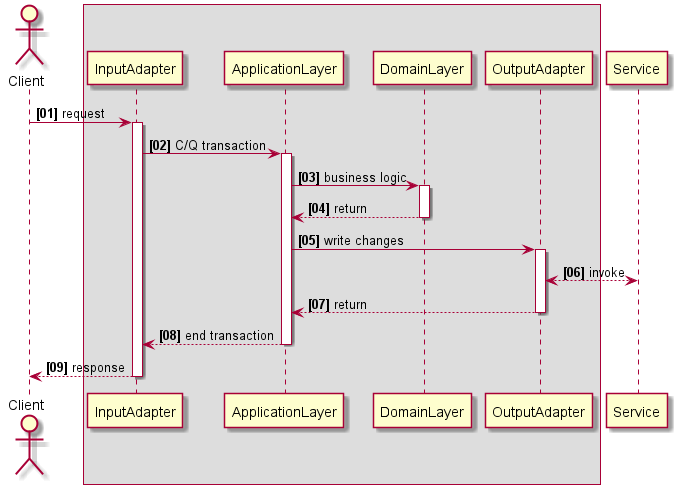
序列图
源码演示
通过一个简单客户信息管理(增删改查)来演示以上叙述中的一些概念。这里使用spring-web实现REST API,通过内存HashMap实现领域对象存储与检索。
新建Customer领域模型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public class Customer {
private String id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
protected Customer() {
}
public Customer(String id, String firstName, String lastName) {
this.id = id;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void changeFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
}
|
实现应用层服务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| @Component
public class CustomerApplication {
private CustomerRepository repository;
@Autowired
public CustomerApplication(CustomerRepository repository) {
this.repository = repository;
}
public void create(CreateCustomerCommand command) {
Customer customer = new Customer(UUID.randomUUID().toString(),
command.getFirstName());
repository.add(customer);
}
public Object fetch(String id) {
return repository.get(id);
}
public void changeFirstName(String id, String firstName) {
Customer customer = repository.get(id);
assert customer != null;
customer.changeFirstName(firstName);
repository.update(customer);
}
public Collection<?> all() {
return repository.all();
}
}
|
实现输入接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| @RestController
public class CustomerController {
private CustomerApplication application;
@Autowired
public CustomerController(CustomerApplication application) {
this.application = application;
}
@PostMapping("/customer")
public ResponseEntity<Object> create(@RequestParam String firstName) {
application.create(new CreateCustomerCommand(firstName));
return ResponseEntity.ok(null);
}
@GetMapping("/customer/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Object> get(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(application.fetch(id));
}
@PatchMapping("/customer/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Object> changeFirstName(@PathVariable("id") String id,
@RequestParam String firstName) {
application.changeFirstName(id, firstName);
return ResponseEntity.ok(null);
}
@GetMapping("/customers")
public ResponseEntity<Object> all() {
return ResponseEntity.ok(application.all());
}
}
|
定义仓储接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public interface CustomerRepository {
Customer get(String id);
void add(Customer customer);
void update(Customer customer);
Collection<Customer> all();
}
|
实现仓储接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| @Component
public class InMemoryCustomerRepository implements CustomerRepository {
Map<String, Customer> customerMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public Customer get(String id) {
return customerMap.get(id);
}
@Override
public void add(Customer customer) {
customerMap.put(customer.getId(), customer);
}
@Override
public void update(Customer customer) {
customerMap.put(customer.getId(), customer);
}
@Override
public Collection<Customer> all() {
return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(customerMap.values());
}
}
|










